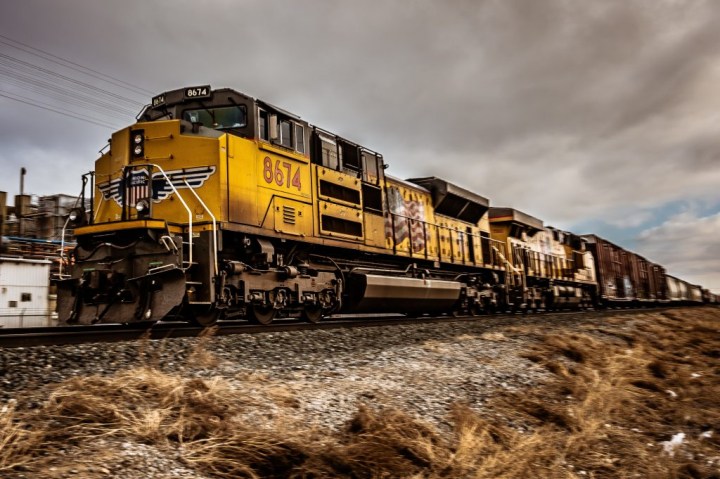
The railroad network in the United States consists of thousands of miles of tracks, transporting the people, food, and goods necessary to support the American economy. To keep the cargo safe and avoid collisions, rail operators require an airtight system of automatic controls and verbal communication via two-way radio.
Railroads adopted electronic communication quite early with the telegraph, moving to the radio shortly after. Following World War II, radio technology had progressed to the point where VHF was a practical solution for industry wide use. Radio remains one of the top communication methods for railroad employees today, offering handheld two-way radio solutions coupled with advanced accessories to ensure maximum safety.
While two-way radio still offers dominance in rail communications networks, new technologies are beginning to take shape. Cellular transmission is gaining steam for example, to the point where companies provide mobile devices to employees fitted with specially made applications. Wi-fi also looks promising, as it can provide connectivity in remote areas where cellular is unavailable, Check out the best internet and phone service.
Another popular use of telecommunications in the train industry is the signaling system known as communications-based train control (CBTC), which uses the connection between the train and track equipment to manage traffic on the tracks. These automatic controls make for more efficient traffic management, but also come with some risks.
Two-Way Radio Use In The Rail Industry
According to the National Transportation Safety Board, poor communication is a critical factor in most rail accidents. Many crews are using outdated equipment, which often leads to problems including poor sound quality, spotty coverage, and weak two-way radio battery life.
To avoid miscommunication and prevent errors, rail operators should update their radio and accessories regularly and take protective measures to ensure the longest useful life. Batteries should always be fully charged and removed from the charger once full. Failure to do so will deplete the battery capacity over time and increase risk of the radio battery dying during critical operations.
Surveillance kits are popular accessories in the industry, as they allow the operator to hear instructions and updates without interference from the loud noises from the train. Earpieces are another popular accessory for railroad employees, allowing people such as controllers to operate their radios hands-free.
Going forward, railroaders are looking to replace old radios with digital technology. One of the biggest challenges in the industry today is the volume of information being transmitted, calling for more efficient technologies. Motorola has introduced a new digital radio called MOTOTRBO that’s gaining traction in the rail industry, along with Kenwood’s NEXEDGE G Series. Both radios are designed for critical business communication needs and operate using licensed spectrum.
Wi-fi & Cellular Communication
Beyond two-way radio, railroads are also beginning to utilize wi-fi and cellular technologies to communicate, especially in remote areas. Recently, cellular networks have grown in popularity among railroads due to their convenience, ease of operation, and low maintenance requirements. For example, some uses include downloading information from equipment inspection systems, access track authorities, and track inspection requests.
Where many railroads provide their workers and conductors cellphones to communicate, a few companies are even deploying mobile applications. CSX Transportation has created an onboard wireless reporting system for conductors, as well as other apps for signal maintainers, truck drivers, and more.
In remote locations, railroads are looking to wi-fi to meet their communications needs. Because remote areas often lack access to cellular networks, some companies are building their wi-fi networks as a backbone to transmit information back to yard crews.
These technologies hold promise for the industry, however they are still very new and untested. The most popular method of communication remains the two-way radio, which has had a reliable infrastructure built up over the years. This network allows universal communications across the entire railroad system, a capability that railroad companies are very hesitant to give up for newer technologies.
Communications-Based Traffic Controls
Traditionally, tracks operated on fixed block systems, wherein each section of the track is known as a “block.” Each block is protected by a signal, which prevents another train from entering an occupied block. CBTC on the other hand, is a moving block system where the “block” is the train itself, and moves with the train. This way, the train’s exact position can be tracked continuously via radio without interruptions.
This technology has been improved upon over the past 30 years, with experience making CBTC less prone to failure than previous systems. Moreover, CBTC requires less monitoring equipment with better diagnostics, which allows easy implementation and better maintenance. Coupled with modern electronics, these systems are also much more energy efficient due to their autonomous nature.
In terms of risk, the primary one is that the system would have to enter a failsafe state if the communications link between any of the trains is disrupted and remain that way until there is a fix. Furthermore, if the situation is severe enough, effects can include temporary loss of train speed, or even the train coming to a halt. These risks call for a contingency plan to be established, consisting of either a manual operation or fixed block.
Communications are an essential part of the railroad industry, serving as the medium through which cargo and people safely move from point A to point B. Physical communications are primarily over two-way radio because of the reliable infrastructure which has been put in place. As a result, employees should not expect the technology to become obsolete any time soon. However, cellular networks and wi-fi connections can provide much longer range communication than radio, which is necessary for lengthy journeys. In terms of autonomous systems, CBTC is very useful in making sure the train is running efficiently and on time, avoiding dangerous situations and keeping the cargo safe. CBTC also monitors the train’s systems to make sure everything is running smoothly, and allows tracking via radio for outside operators to monitor. In conclusion, there are a wide variety of communication methods and technologies implemented in the railroad industry to make sure goods and people can reach their destinations safely. The digital age has brought about new ways to communicate, however the dominant method remains the two-way radio due to its dependability.
Finding Help with Moving Professionals
We hope you found this blog post on Importance of Communication for Railroads useful. Be sure also to check out How Transportation Has Upgraded Over the Years for more great information!
Need to Move Furniture? With All Around Moving you don’t need to worry about any unexpected charges. We are always upfront about our prices and take pride in taking care of every need of our customers before and during the move. For a stress-free move where you don’t need to take care of anything contact us today! We are “A+” rated members of the Better Business Bureau and a member of Greater New York Chamber of Commerce & Miami Dade
Discover how uniquely priced we are compared to other moving companies in New York, NY & Miami, Florida. Get a moving quote specifically tailored to your moving needs by calling us TODAY!
Have Experience in the Moving Industry? Want an Additional Income Stream? Work With All Around Moving!
All Around Moving’s Work With Us program provides experienced moving consultants with the opportunity to run their own Relocation Consultant business from anywhere in the USA. We provide licensing, dedicated phone lines and email hosting, moving software for lead tracking, invoicing, and complete set up.
We’ll even provide the carriers, or you can use your own. A nominal one-time start up fee gives you initial-customer-leads to get your business up and running. There are no recurring expenses, except purchasing your own leads. We share profits 50-50 with you from all jobs you book with us. Click here to learn more.